Mitochondrial health promotes cellular energy (ATP) production and contributes to the dynamic equilibrium between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant defense systems within the body’s cells. Beyond ATP synthesis, mitochondria are involved in and direct essential cellular processes that help maintain cellular integrity, such as signaling pathways, mitophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis. These core functions—cellular energy production, oxidative balance, and mitochondrial renewal—are foundational to women’s wellness throughout adulthood.
Ubiquinol—the active antioxidant form of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)—is naturally present in the body and supports mitochondrial function. It participates in cellular energy generation and helps protect cells from oxidative stress. It contributes to the maintenance of healthy mitochondrial efficiency and manages cellular and tissue homeostasis, all of which influence processes tied to women’s wellness, such as healthy aging and cardiovascular and reproductive health.
In this blog, we’ll explore how mitochondrial function relates to women’s health and discuss the potential role of ubiquinol in supporting women’s wellness throughout life stages.
Key Functions of Mitochondria
Signaling Pathways
The way mitochondria communicate with and modulate other parts of the cell, tissues, and organs to manage essential functions such as repair, programmed cell death (apoptosis), senescence (where cells stop dividing but remain metabolically active), immune system activity, and energy balance.
Why it matters: These signals direct cells to adapt to internal and external stressors and are central to how the body coordinates cellular homeostasis, repair, and immune response, all of which impact women’s health at every stage of life.
Mitophagy
The process by which cells remove damaged mitochondria to help maintain mitochondrial quantity, quality and location to support cellular health.
Why it matters: Mitophagy helps sustain efficient energy production, reduce excess oxidative stress, and preserve cellular balance—factors that are crucial for long-term cellular resilience and proper function.
Mitochondrial Biogenesis
The formation of mitochondria within cells in response to increased energy demands or physiological signals—such as exercise, nutrient availability, and mild stress—that prompt cells to enhance energy production.
Why it matters: More mitochondria are sometimes needed to generate more energy capacity—key for women during life phases of hormonal fluctuation, stress, or increased metabolic demand.
The Importance of Oxidative Balance in Mitochondrial Health
Mitochondria convert sugars, fats, and proteins into the energy molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), producing approximately 95% of the energy needed for cellular activities.1 However, mitochondria are also the primary source of ROS, which are created as a byproduct of energy generation. ROS and other free radicals can also enter the body from the environment, including from exposure to pollution or UV radiation, and are associated with lifestyle factors, like diets low in nutrients, inactivity, smoking and alcohol consumption.2
ROS are unstable molecules that contain an unpaired electron. They attempt to stabilize themselves by snatching electrons from other healthy molecules. Antioxidants help protect against such thefts by donating an electron to ROS, neutralizing them before they cause damage. Oxidative stress occurs when the production or accumulation of ROS exceeds the body’s antioxidant defenses. If not brought under control, oxidative stress can damage cell components, including membranes, tissues, proteins, and lipids.3,4
The presence of excess ROS within the mitochondria is a concern, as oxidative stress can impact the health of the mitochondria themselves. Oxidative stress can affect the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) as well as the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC). Oxidative damage to the ETC can lead to a decrease in ATP production and an increase in ROS generation, causing a cycle of damage. Such damage may impair mitochondrial function and can lead to cellular damage and even cell death, contributing to processes commonly associated with aging.3,4
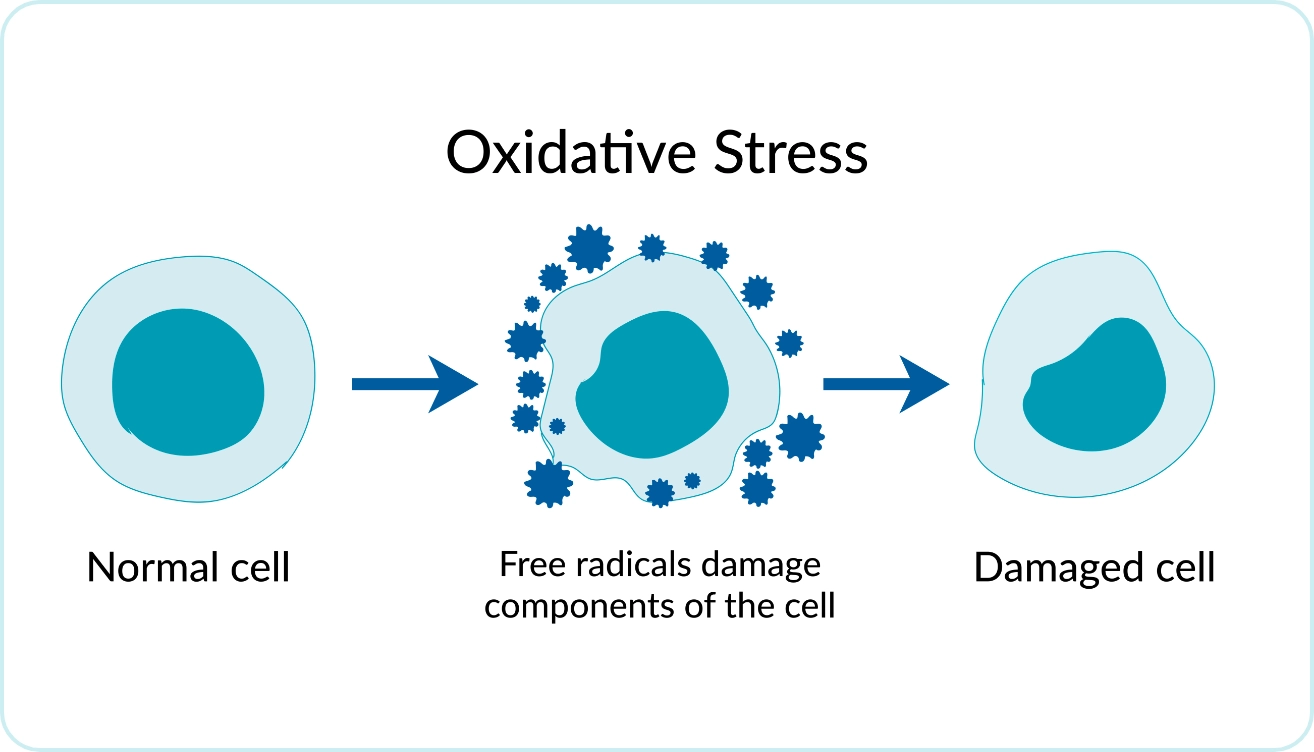
How Mitochondrial Health and Oxidative Stress Influence Women’s Health
Women’s cellular energy demands are uniquely influenced by reproductive biology, perimenopause, and menopause. The different physiological demands during these stages require mitochondria to respond to varying levels of oxidative stress and support energy-intensive processes, such as reproductive and cardiovascular function. The mitochondria’s role in managing key homeostatic functions throughout life has a significant impact on how women’s cells perform, age, and maintain overall health.
Reproductive Health: Mitochondrial function is particularly important to the reproductive system due to its high energy demands. Oxidative stress may affect mitochondrial efficiency and function, potentially influencing oocyte and egg health.5,6
Menopausal Health: Beyond its other roles, estrogen acts as a natural antioxidant and aids in defending cell membranes and LDL cholesterol from oxidative damage. As estrogen levels decline during perimenopause and menopause, so does this inherent protection. Decreased estrogen is thought to contribute to the increase in oxidative stress often observed in menopausal women.7
Cardiovascular Health: Research suggests that reduced mitochondrial function and increased oxidative stress that may occur during and after menopause, among other factors, are relevant to changes in lipid profiles impacting cardiovascular health.8 Mitochondrial function is especially relevant in heart health due to the high energy demands of the heart, which relies on giant mitochondria to produce the ATP necessary to continually pump blood through the body. Oxidative stress has also been linked to the oxidation of LDL cholesterol and cell membranes, both of which can influence vascular health and endothelial function.9,10
Healthy Aging: Over time, oxidative stress may affect mitochondrial function and DNA integrity, influencing how cells produce energy and maintain homeostasis.11,12 Oxidative damage can accelerate processes like apoptosis and senescence, contributing to tissue aging and changes in cellular function observed with the aging process.
Antioxidants as a Cornerstone of Women’s Health
Ubiquinol is the active antioxidant form of CoQ10 and the only lipid-soluble antioxidant naturally produced in the body. Its lipid solubility allows ubiquinol to penetrate the mitochondrial membranes, where it supports the generation of ATP and helps neutralize ROS at the source.4
With age, the body’s antioxidant defenses decline, and the ability to convert ubiquinone (CoQ10) to ubiquinol diminishes, which may result in lower levels of ubiquinol in the blood.13 For women, menopause-related hormonal changes may further affect antioxidant capacity, compounding the effects of oxidative stress on energy production and cellular health.7 This is when supplementation becomes especially beneficial.
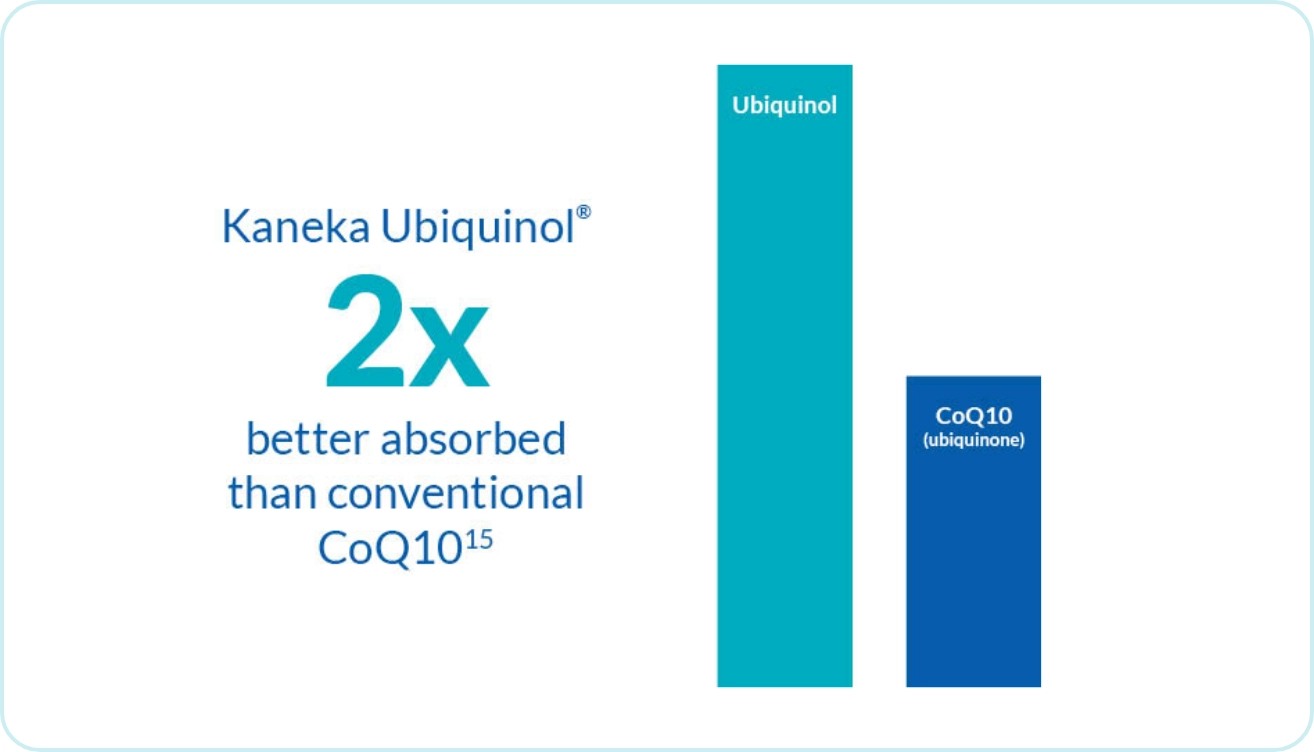
Unlike conventional CoQ10 supplements, Kaneka Ubiquinol® requires no conversion in the body to provide potent antioxidant protection at the cellular level.14 Kaneka Ubiquinol® is bioidentical to the body’s natural ubiquinol and has been shown to be two times better absorbed than conventional CoQ10 when taken as a supplement.15
In a clinical trial, Kaneka Ubiquinol® was shown to increase baseline ubiquinol levels by eight times in healthy adults taking 200 mg for at least 30 days.16
Choose Kaneka Ubiquinol® to support women across life stages:
- Promoting preconception wellness: Ubiquinol supplementation promotes female preconception health by supporting healthy mitochondrial function essential for the health of the oocyte and egg, and mitigating excess ROS that can damage reproductive cells.
- Supporting menopausal well-being: Kaneka Ubiquinol® supports general health and well-being during and after menopause.17,18 In a consumer use study, 80% of menopausal women taking 200 mg of Kaneka Ubiquinol® per day reported decreased irritability, sensitivity, stress, and mood swings after 60 days of supplementation.18
- Promoting healthy aging processes: Supplementation with Kaneka Ubiquinol® has been shown to increase plasma ubiquinol levels. A healthy ubiquinol/CoQ10 balance in the blood is associated with cardiovascular health, muscle health, and physical functioning in older adults.19-21
- Supporting cardiovascular health: Adequate ubiquinol levels correlate with improved blood markers associated with heart health.22-25 Research has found that Kaneka Ubiquinol® supports vessel health and protects LDL cholesterol from oxidation.19
Kaneka Ubiquinol®—An Ally in Women’s Wellness Throughout Life Stages
The link between mitochondrial health, oxidative stress, and overall well-being underscores the critical role ubiquinol supplementation can play in women’s health. In this context, Kaneka Ubiquinol® offers rigorous scientific research and clinical experience in numerous areas that confirm its safety, efficacy, and benefits for overall health. It is backed by over 50 years of ubiquinone and ubiquinol testing and research, 85 human clinical studies using Kaneka Ubiquinol®, and 17 years of positive consumer experience with Kaneka Ubiquinol® supplementation.
As a trusted leader in ubiquinol production in the United States, Kaneka Nutrients ensures the quality, reliability, and purity of Kaneka Ubiquinol®, delivering the safety, performance, and scientific edge consumers demand. Connect with us to enhance supplement offerings and set a new standard in women’s wellness.
Related Posts
NutraIngredients – Apr 5, 2024
Nutraceuticals World - Sep 16, 2024
SupplySide Supplement Journal - Sep 20, 2024



